3 Steps for our Walk-In Service
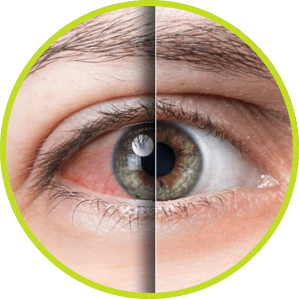
If you have an urgent eye concern or need continued care, please follow the steps below to use our walk-in services:
- Call our Urgent Care office at (403) 526-2020
- Allow us to advise the wait times or the best times to arrive.
- Come visit our office at 444 4th St. SE in Medicine Hat and meet with a doctor today!